FOB – FREE ON BOARD (INCOTERMS 2020)
1. Definition:
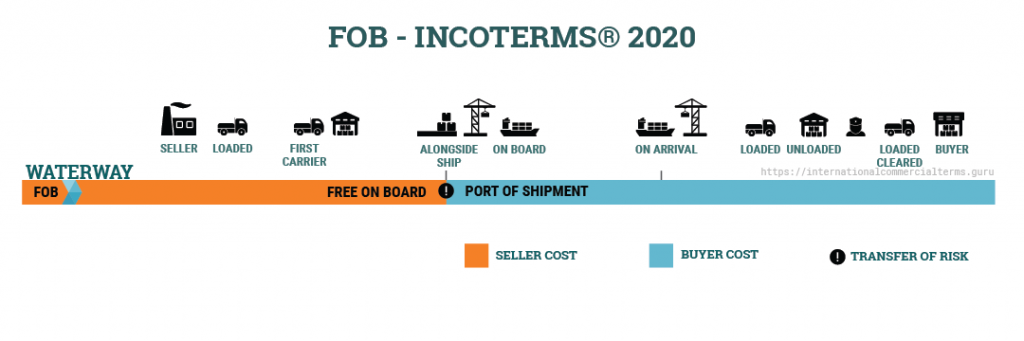
By using FOB the seller must clear the goods for export and delivers when the goods pass the ship’s rail at the agreed port. This term is only used for water transportation either sea or inland water. If both parties do not agree to have goods delivered on board, then FCA is the term to be used.
2. How to use this term:
This term was commonly used when commodities were sold and the carrier confirmed the reception of goods “on board”. When goods are packed in containerized cargo, then FCA is the most recommended term to use. Because goods will be delivered in the container terminal prior to being loaded on the vessel. The term is used in commodities like oil, bulk cargo or grain. There is a common misuse of this term when goods are loaded onto a truck, in that case FCA is the right term to use. In FOB, origin terminal handling charge and all other costs associated to move the goods on board are paid by the seller.
FOB suits better for bulk cargo and not containerized cargo (use FCA instead). FOB can only be used for ocean transportation, the seller’s responsibility ends when the goods are placed on board of the vessel. All cost after loaded onboard must be assumed by the buyer.
Export customs clearance and origin terminal handling charge must be assumed by seller. This term is traditionally created for bulk transportation, where some cargo can be lost during the process of loading (i.e. grains taken away by wind or boxes dropped in the ocean). It is still the most misused term.
3. Seller and Buyer obligations:
-Seller Obligation:
1. General
The seller must deliver the goods, commercial invoice, and any evidence of conformity.
2. Delivery
Deliver the goods by placing on board the vessel nominated by the buyer at the loading point, in the agreed date or period. In a customary manner at the port
3. Risks
All risk of loss/damage until goods have been delivered
4. Carriage
No obligation to make a contract of carriage. Provide at buyers risk and cost, information for arranging carriage. If agreed, the seller must contract the carrier.
5. Insurance
No obligation. Provide at buyers risk and cost, any required information.
6. Delivery/transport document
Proof of delivery at sellers cost and a transport document if arranged by seller
7. Export/Import clearance
All export clearance expenses (license, security, inspection, etc). Assist with import clearance
8. Checking
The seller must check, count, weight, mark, and package goods
9. Allocation of cost
Pay all the cost until delivery. Cost of proof of delivery. Duties and taxes for export. All costs related to providing assistance in obtaining documents to the buyer
10. Notices
Give notice that goods have been delivered or the vessel failed to collect the goods.
– Buyer Obligation:
1. General
The buyer must pay the price of goods as agreed.
2. Taking Delivery
The buyer takes the goods after delivered.
3. Risks
All risk of loss/damage from the time or end of the period agreed for delivery. If the buyer fails to nominate a carrier, or if the carrier doesn’t arrive, the risk is under the buyer.
4. Carriage
Contract the carriage from the place of delivery unless agreed the seller will contract the carrier.
5. Insurance
No obligation to insure the goods.
6. Delivery/transport document
Accepts the proof of delivery
7. Export/Import clearance
Assist with export clearance. Pay for import clearance and formalities (licenses, security, official documentation).
8. Checking
No obligation.
9. Allocation of cost
Pay from the time goods delivered. All costs for assistance on getting carriage, insurance, delivery, and customs documentation. Pay duties and taxes for import or transit. Any additional cost if the carrier is not nominated or carrier fails to collect goods.
10. Notices
Notify the vessel name, loading point and time or period.
Please contact Airport Cargo to be further information.
Read more:
The challenges of cross-border international trade – (airportcargo.vn)


